Quantitative metrics in IT are good when work is:
- input-output processing
- high frequency
- standardized outputs
- predefined process or workflow
For example request fulfilment, access management, standard changes, routine incidents
As most regular work in IT is automated, work characteristic is drifting toward non-regular, ever changing knowledge work so applicability of quantitative metrics is in decline.
Examples of knowledge work:
- learning, communication,
- exploration
- improvement and innovation effort
- security
- data integration and complex APIs
Qualitative metrics are enabling consolidated perspectives, retrospective quality analysis and understanding of the big picture.
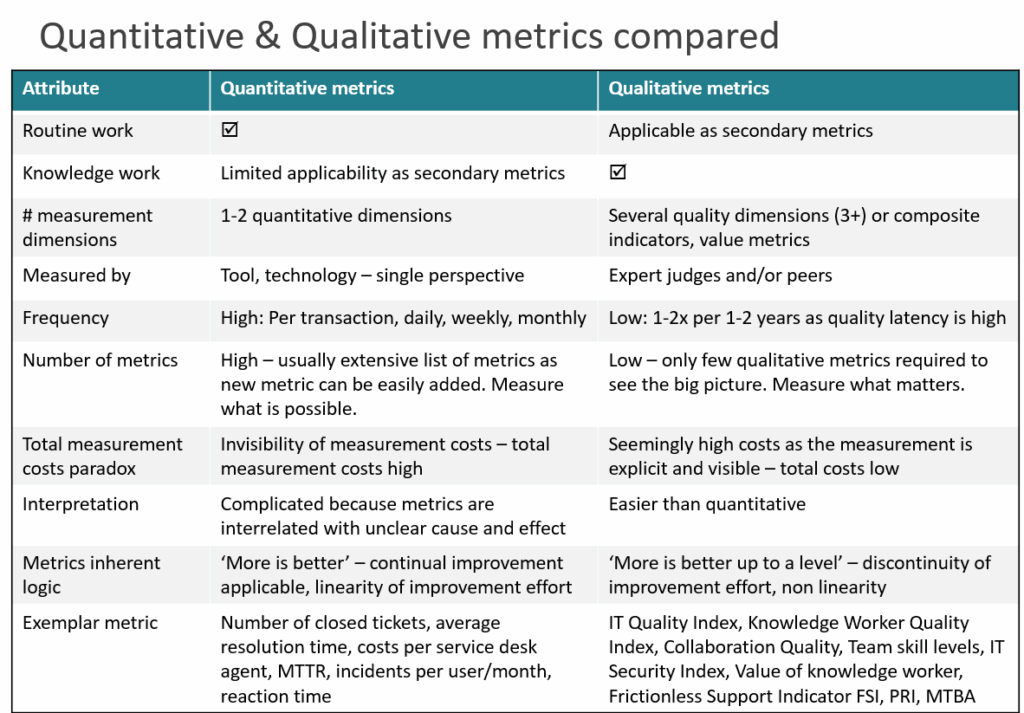
We live in post-industrial era, most workers are knowledge workers, thus drift to qualitative management is inevitable.
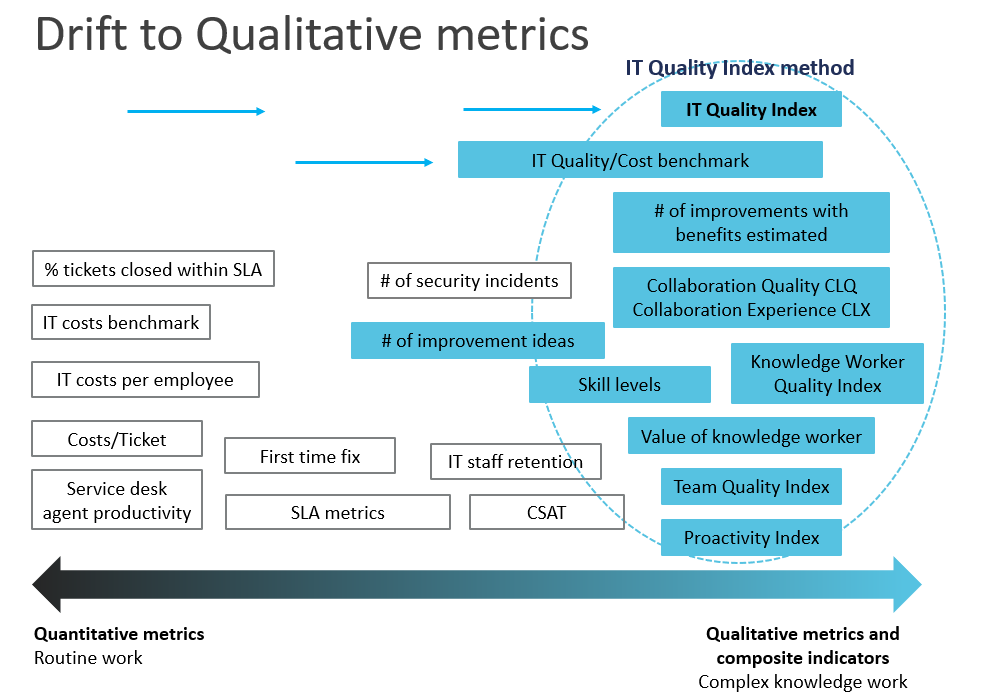
From practical perspective we can decrease frequency and complexity of quantitative measurement and metrics and use less, more meaningful qualitative metrics.
Practical guidance how, including selection of suitable qualitative metrics are part of IT Quality Index method, for example Collaboration Quality, Knowledge Worker Quality Index, Collaboration Experience, Frictionless Support Indicator etc.