SFIA 8 defines 121 skills covering almost all activities relevant to internal IT departments or external service providers. Vast majority of described skills are proactive, non-repetitious, complex, when people don’t follow strictly defined processes or workflows.
From Quality management perspective, the core skill is Quality Management – Defining and operating a management framework of processes and working
practices to deliver the organisation’s quality objectives.
Practical adoption of Quality management means:
- Skilled people, who know what quality is really
- Assessment of actual quality level
- Definition of target quality level
- Adoption of IT QMS tracking quality changes of all aspects of IT work
- Visual management and communication
IT Quality Index body of knowledge is providing a practical guidance how quality management can be adopted.
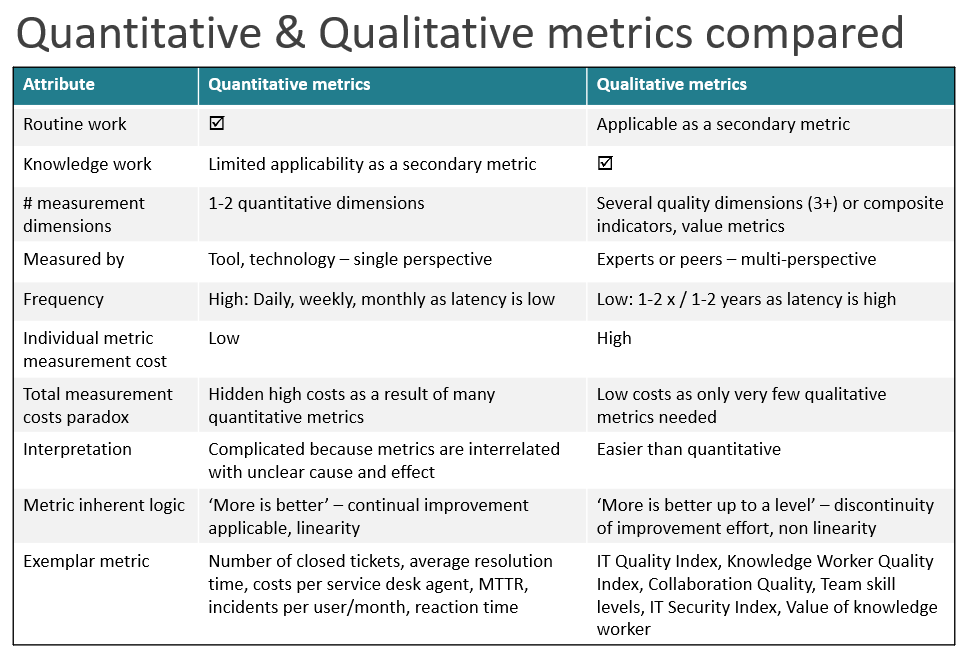
Quality management is an attribute of proactive quality focused IT governance, where people prioritize quality over quantity. Quality management also leads to reduction of quantitative metrics and introduction of very few qualitative metrics as IT Quality Index, Collaboration Quality, Collaboration Experience or Knowledge Worker Quality Index.
Quality management skills is frequently missing in many IT departments, who adopted passive, demand driven mode of working. Quality is recursive – quality starts when quality management is introduced.
Typical steps of quality management adoption are here.